Visual Minteq
MWH s Water Treatment Principles and Design, Third Edition. Tutorial on Visual Minteq 2.50 operation and input/output for simple problems related to acid/base pH and titrations. Generally, it is recommended that you work problems that you are already familiar with, to see how the program works –open all the buttons and windows with a known problem, for example the pH of 0.001 M NaH 2 PO 4 in water at 25 C is 5.13, neglecting activity coefficients. PHREEQC and Minteq are among publicly available water chemistry programs that provide a variety of parameters including activity coefficients. PHREEQC has a coupling feature that allows developers to easily integrate it into their models. Although accessibility to thermodynamic models gives tremendous benefits, discrepancies may occur as. Western Michigan University has made several campus computer labs available to access remotely from your own computer anytime, anywhere. Follow the instructions below to learn how to connect to our computer labs remotely, as well as a list of software available on each remotely accessible lab.
Visual Minteq Software

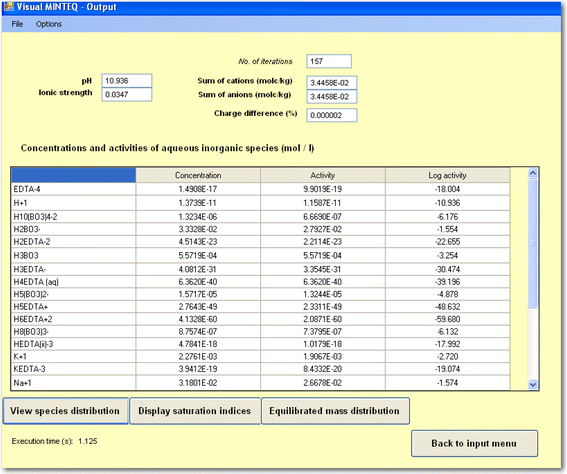


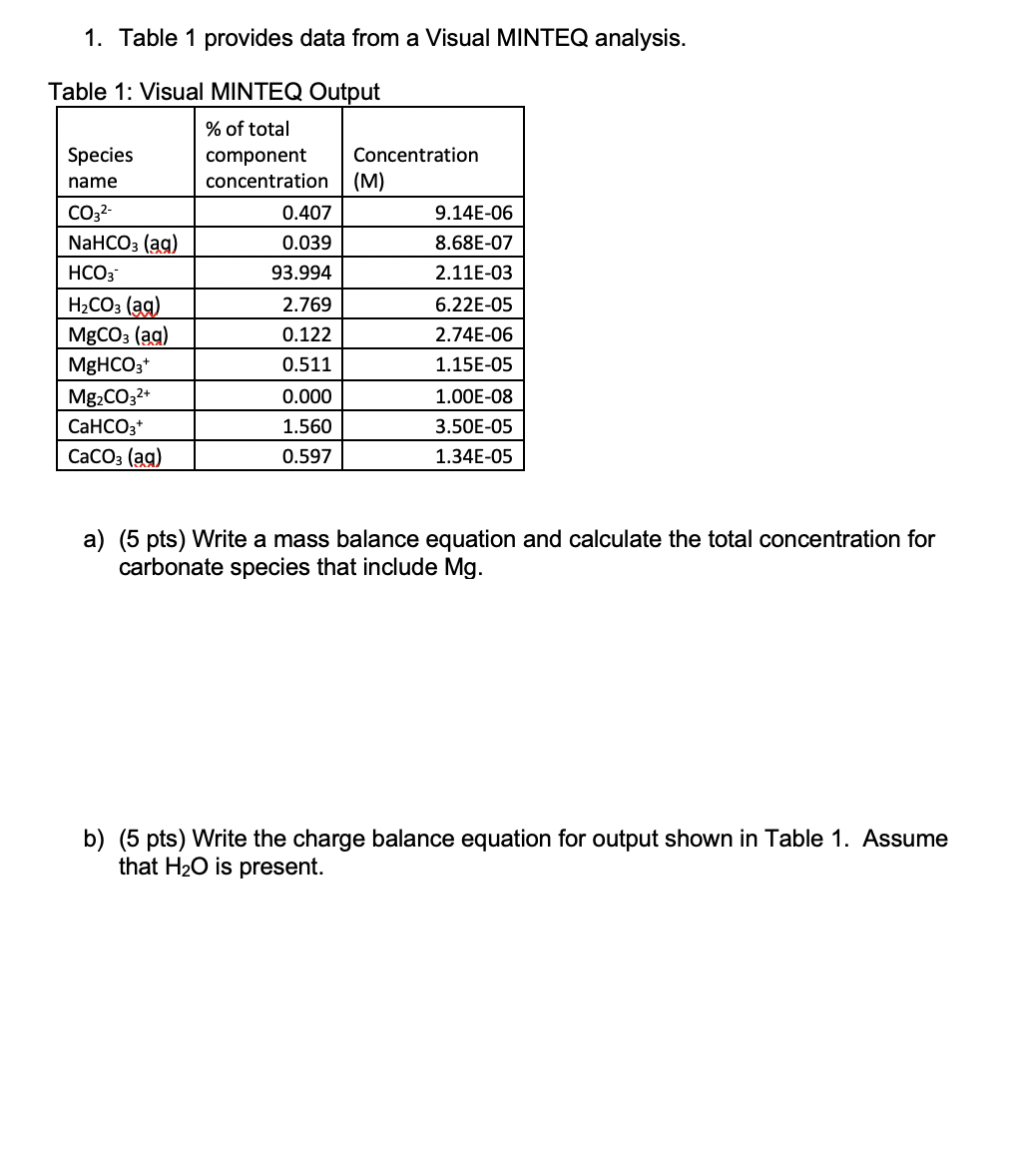
Visual Minteq Titration
| The LLNL thermo database. This is the default dataset of thermodynamic data for the GWB applications, including log Ks for hundreds of reactions involving aqueous species, minerals, and gases; also coefficients for evaluating activity coefficients by the B-dot equation. | thermo.tdat [or GWB12 format] |
| An expanded variant of the LLNL database containing many organic species and radionuclides. Some people feel this database is less internally consistent than thermo.tdat, especially with respect to aluminum and sulfur species. | thermo.com.V8.R6+.tdat [or GWB12 format] |
| The thermodynamic dataset from Release 2.8 of the USGS's PhreeqC program, formatted for the GWB applications. (You can use TEdit to convert more recent PhreeqC databases to GWB format.) | thermo_phreeqc.tdat [or GWB12 format] |
| Visual Minteq's thermodynamic database, formatted for the GWB courtesy of Jon Petter Gustafsson. Updated versions may be available from his website. | thermo_minteq.tdat [or GWB12 format] |
| Thermo data from the USGS's Wateq4F software. | thermo_wateq4f.tdat [or GWB12 format] |
| Log Ks and virial coefficients for evaluating the Harvie-Møller-Weare activity model (a formalism of the “Pitzer equations”) at 25°C | thermo_hmw.tdat [or GWB12 format] |
| The Harvie-Møller-Weare activity model, as implemented in the USGS program PHRQPITZ. The dataset includes borate species and limited provision for temperature dependence. | thermo_phrqpitz.tdat [or GWB12 format] |
| The Yucca Mountain Project dataset, invoking the Harvie-Møller-Weare activity formalism of the “Pitzer equations” | thermo_ymp.R2.tdat [or GWB12 format] |
| The THEREDA project's database incorporating high-temperature “Pitzer” activity coefficients | thereda_2020_gwb_jan19.tdat [Release Notes] |
| The Thermochimie project's database invoking the SIT activity model | thermo_sit.tdat |
| The Nuclear Energy Agency’s thermochemical database using the SIT method | thermo_nea.tdat |
| The FREZCHEM “Pitzer” database valid to very low (sub-zero C) temperature, as set out by Toner and Sletten | thermo_frezchem.tdat |
| COLDCHEM low-temperature (sub-zero C) “Pitzer” database, from Toner and Catling | thermo_coldchem.tdat |
| The Cemdata18 thermodynamic database for hydrated Portland cements and alkali-activated materials, from Lothenbach et al. | thermo_cemdata.tdat |