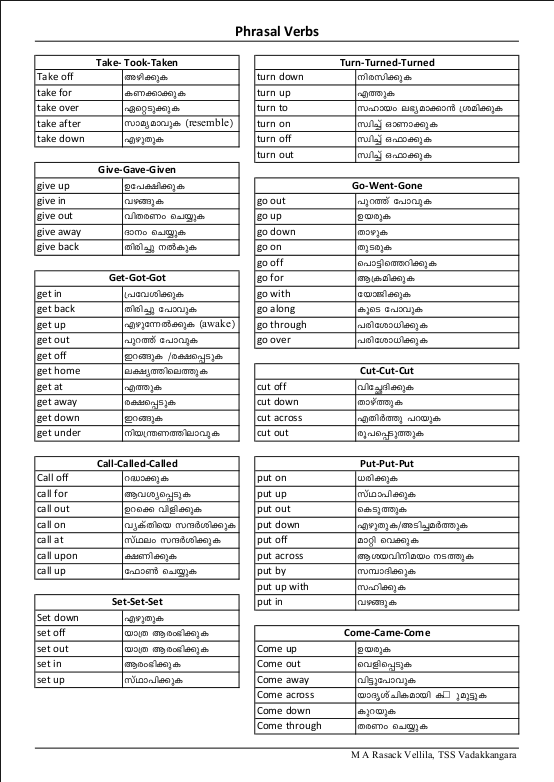
Phrasal Verbs List With Malayalam Meaning
There are some verbs in English that combine with propositions or adverbs to gain new meaning. Such
- Phrasal Verbs List With Malayalam Meaning
- Phrasal Verbs List With Examples
- Phrasal Verbs List Pdf
- Get Up Meaning Phrasal Verb
- Phrasal Verbs List With Malayalam Meanings
A phrasal verb is a verb followed by a preposition or an adverb; the combination creates a meaning different from the original verb. Alphabetical lists of commonly-used phrasal verbs in English. Alphabetical List - A.
Verb + Proposition- Phrasal verbs are verbs with a preposition, adverb or both. The meaning differs from the original verb. Here, you will find a list of common phrasal verbs in the English language and tips on word order. Learn about phrasal verbs in English grammar online with Lingolia. In the free exercises, you can practise what you have learnt.
- Phrasal verbs list from A to Z with examples in PDF. To choose a list of phrasal verbs click on a letter of the alphabet and a list of all the phrasal verbs will appear for that letter. Phrasal verbs in PDF youu can download for free just click on this link. Phrasal verbs list from A to Z.
These are the lists of Phrasal Verbs –
1. ask for – demand, to somebody
Can I ask you a question?
I always ask for extra butter on bread.
2. back up – support
Make sure you back up every day.
You’ll have to back up and turn around.
3. bear with – tolerate patiently
If you will bear with me, I shall be very glad.
Please bear with me.
4. blow out – extinguish by blowing
When the window opened, the wind blew out the candle.
The electric fire has blow out.
5. blow up – explode
Suddenly the bomb blew up.
Can you help me blow up these balloons?
6. boil over – boil and flow over
The milk is boiling over now.
The situation was about to boil over.
7. break down – fail, stop
It takes a long time to break down prejudices.
The television has broken down.
8. break in – enter by force
There is a break in the gas pipe.
Children shouldn’t break in on adult’s conversation.
9. break out – start suddenly
The fire broke out at early morning.
He predicted when war would break out.
10. break up – end
The meeting broke up at 10 o’clock.
I want to break up with you.
11. bring forth – produce something
Trees bring forth fruit.
April showers bring forth May flowers.
12. bring up – raise
We need to bring up more candidates.
It’s hard for the baby to bring up wind.
13. bring out – open, publish
The spices really bring out the flavour of the paneer.
The sunshine will bring out the blossom.
14. call in – convene
Please call in a doctor immediately.
How many guests will you call in?
15. call off – cancel, withdraw
The commander decided to call off the attack.
The strike will be called off tomorrow.
16. call up – recall
We call up the arrow on the screen with the keyboard.
He is going to call up and cancel his subscription.
17. call for – require, demand
Let me transfer this call for you.
I’ll call for you at five.
18. call out – summon
I had to call out an electrician.
Let’s call out for pizza.
19. care for – like somebody
He does not care for his wife.
She cares for her children deeply.
20. carry out – execute, obey
You must carry out my orders.
He did not carry out his promise to us.
21. carry on – continue
How long can this situation carry on?
We must carry on hoping for the best.
22. catch on – become popular
It could catch on fire easily.
It’s not that hard, once you catch on to it.
23. clear up – make clean
Please, clean up the table before you leave.
Could you please clean up the living room?
24. clear away – pass away, remove
Clear away your utensils now.
We must clear away the misunderstanding.
25. clear off – go away
I am clear off the debt soon.
The morning mist will clear off soon.
26. come out – be published
Come out and get some fresh air.
When do the exam results come out?
27. come on – come with
Come on, wake up, we will late.
I can’t come on that date.
28. come down – become lower
He had come down with the fever.
Come down from there this minute!
29. cut down – reduce
Cut down your expenses.
Do not cut down the tree that gives you shade.
30. cut off – disconnect
The telephone wire is cut off in this house.
He cut off a small piece of bread.
31. deal in – sell something
We deal in software.
They deal in antiques.
32. dispose of – finish
They had to dispose of the opposition.
Dispose of these old television.
33. do away with – abolish
She tried to do away with herself.
He told me to do away with this old hat.
34. do without – manage in absence of someone
I can do without your advice.
You can do without all that hassle.
35. draw back – recoil
It may already be too late to draw back.
If you take part in the race, you mustn’t draw back.
36. fall off – decrease
The number of students has fallen off.
Be careful not to fall off the ladder.
37. fall out – quarrel
The drugs made her hair fall out.
I don’t like to fall out with my friends.
38. fall back – withdraw
If I lose my job, I’ll have nothing to fall back on.
At last, the enemies had to fall back.
39. fall on – attack violently
I held the belief that we would fall on our feet.
Prices continued to fall on the stock market today.
40. find out – to search
I was curious to find out what he had said.
How did you find out about the party?

Related Posts
Daily Greetings and Polite ConversationSmall Sentence (Hindi to English)
English Exclamatory Sentence Examples (Hindi to English)
Imperative Sentence Examples (Hindi to English)
Preposition list with examples
Modal auxiliary verbs with examples
Degree of Comparison – Comparative and Superlative Examples
Active Passive Voice with Examples
Phrasal Verbs II – list, meaning, example
Proverbs in English and Hindi
Idioms and Phrases with meanings and examples
Related Pages
Phrasal Verbs
A phrasal verb is a multi-word verb made up of a main verb and at least one preposition or a particle that changes the meaning of the verb from the original verb.Easy Examples of Phrasal Verbs
- to break in (The main verb is 'to break.' The preposition is 'in.' The phrasal verb is to 'break in,' which has a different meaning to 'to break.')
- to catch up
- to blow up
- to break down
- to cut back
- to put up with
- to go out with
- to check up on
- to cut down on
Real-Life Examples of Phrasal Verbs
In these examples, the phrasal verbs are shaded.- Damn your principles! Stick to your party. (Prime Minister Benjamin Disraeli)
- When people find out you're an actress, they Google you. (Actress Laverne Cox)
- Meditation helps me to calm down. (Singer Lady Gaga)
- Do I exaggerate? Boy, do I, and I'd do it more if I could get away with it. (Comedian David Sedaris)
There Are Transitive and Intransitive Phrasal Verbs
Some phrasal verbs are transitive (i.e., they can take a direct object), and some phrasal verbs are intransitive (i.e., do not take a direct object).Here are some examples of transitive phrasal verbs. (The direct objects are in bold.)
- Fill inthe form as quickly as possible.
- Did you go overthose reports last night?
- I will look intoit immediately.
- I felt compelled to handthe pursein . (Note: Some phrasal verbs are separable. There is more on this below.)
- If you're unhappy, please stand up .
- The lorry is starting to drop back.
- The tree could fall down.
- Do not give in.
- She will show up soon. (This is intransitive. It means 'She will appear soon.')
- She will show up the opposition. (This is transitive. It means 'She will embarrass the opposition.')
There Are Separable and Inseparable Phrasal Verbs
Some transitive phrasal verbs are separable. This means the direct object appears between the verb and the preposition. For example:- I will makeyouup to look like a princess.
- She talkedher fatherinto letting her attend the party.
- She looks up toher sister.
- You must stick tothe plan at all costs.
- He lookedmy addressup on the National Voter Register. (This is the separable way.)
- He looked upmy address on the National Voter Register. (This is the inseparable way.)

- He looked upit on the National Voter Register.
- He lookeditup on the National Voter Register. (That's crazy. Anyway, good luck explaining that if you're an English teacher!)
Is the Accompanying Word a Particle or a Preposition?
A phrasal verb is made up of a verb and an accompanying word (or words). The accompanying word (or words) is classified as either a preposition or a particle. ('Particle' just means 'nothing in particular.' The particles in phrasal verbs are often classified as adverbs, but this description is widely contested...and with good reason. The particle of a phrasal verb doesn't tell us how, when, where, or why the action of the verb is being carried out. It changes the verb's meaning. That doesn't sound very adverb-like.)When the accompanying word introduces a prepositional phrase, it is classified as a preposition. If it does not, it is classified as a particle. For example:
- She takes after her mother. (In this example, the prepositional phrase is after her mother. The word after is a preposition.)
- Please think it over. (In this example, the word over does not introduce a prepositional phrase. Therefore, it is a particle as opposed to a preposition.)
- I can stand in for you next week. (In this example, the word in is a particle but the word for is a preposition as it introduces the prepositional phrase for you.)
Why Should I Care about Phrasal Verbs?
There are three good reasons to avoid phrasal verbs and two good reasons to embrace them.(Reason to Avoid 1) Phrasal verbs sound informal.
Phrasal verbs tend to derive from our Germanic heritage. As the Germanic elements in our language stem from the language of the common people, phrasal verbs are usually easy on the ear and easily understandable for native English speakers. That's all good. The downsides, however, are that phrasal verbs can seem informal and they eat up your wordcount. Therefore, in business and academic writing, there is a leaning towards the one-word Latinate verbs, i.e., those which derive from our French heritage. Latinate verbs sound more formal because they stem from the language of our aristocracy.- We'll all get together in the foyer. (okay, if a little informal)
- We will congregate in the foyer. (preferable in a formal email)
- We've put the meeting off until Tuesday. (okay, if a little informal)
- The meeting is postponed until Tuesday. (preferable in a formal email)
(Reason to Avoid 2) Some phrasal verbs eat up your wordcount unnecessarily.
The merit of Germanic over Latinate words is up for debate, but some phrasal verbs include prepositions or particles that don't add anything. Delete them.Phrasal Verbs List With Malayalam Meaning
- I cannot face up to this problem. (okay)
- I cannot face this problem. (better, more succinct)
- Try this new garlic dip out. (okay)
- Try this new garlic dip. (better, more succinct)
- She will not stand for shoddy work. (okay)
- She will not stand shoddy work. (better, more succinct)
- Even I don't wake up looking like Cindy Crawford. (Model Cindy Crawford) (It is possible to use wake without up, but it doesn't sound as natural.)
(Reason to Avoid 3) A phrasal verb often sticks a preposition at the end of your sentence.
Yeah, it doesn't matter how many times we're told that it's okay to end a sentence in a preposition. There are still wads of people out there - as evidenced by our poll - who think it isn't okay. So, for now, if you can easily avoid ending a sentence in a preposition, you might as well. For one, it's safer, and, two, it's usually more succinct. Think of it as a game, not a rule.- It is a situation I will not put up with. (okay)
- It is a situation I will not tolerate. (safer and more succinct)
Phrasal Verbs List With Examples
- Can you sort it out? (okay)
- Can you resolve it? (safer and more succinct)
(Reason to Embrace 1) A phrasal verb might better fit your image.
When choosing words for business correspondence, you must consider the character of your business. For example, auditors like KPMG might write 'Terms and Conditions of the Contract,' while Virgin Media might write 'The stuff you need to know.' You must know your 'writing voice.' If you're a formal bunch, you should probably steer clear of phrasal verbs, but if you're a down-with-the-kids outfit, phrasal verbs and other simplistic vocabulary will be a better fit.- We would not expect you to tolerate a second-rate service. (corporate)
- Don't put up with bad service. (engaging)
(Reason to Embrace 2) Phrasal verbs are easily understood.
Phrasal verbs are often much clearer than Latinate verbs.- The framework is required to concatenate the disparate elements. (This might sound business-like, but there's a risk it won't be understood.)
- The framework is required to join up each element. (This is much clearer and safer.)
Key Points
Phrasal Verbs List Pdf
- Phrasal verbs sound natural, and they're easily understood. However, they can sound too informal for business or academic writing. Strike the balance you need.
- Sometimes, the preposition that accompanies the main verb in a phrasal verb is unnecessary. If it doesn't add anything, delete it.
Interactive Exercise
Here are three randomly selected questions from a larger exercise, which can be edited, printed to create an exercise worksheet, or sent via email to friends or students.- Do you disagree with something on this page?
- Did you spot a typo?